Haptic Feedback for Surgeons
The world's smallest force/torque sensor enables maximum precision in ophthalmic, dental and abdominal surgery. Robotic systems gain a sense of touch thanks to the development of the joint venture between WIKA and WITTENSTEIN.
Surgical robots in the fields of dental, eye and abdominal surgery must be extremely sensitive to control. The measurement of precise force-torque data close to the end effector or instrument is crucial for this.
Haptic feedback for surgeons
Robotic systems in surgery have been used in practice for decades and are well established. The surgeon does not necessarily have to stand with the instrument next to the patient in order to perform operations. Camera systems are used so that the surgeon can still monitor every step he or she performs. Visual information is a basic prerequisite for the success of the operation.
Haptic feedback is poorly represented in current systems. Information on how hard the instrument is pressing against the tissue or how firm the tissue is is based solely on visual information. By incorporating force/torque sensors, extensive haptic feedback can be fed back to surgeons, giving the robots and therefore the surgeons a sense of touch.
The success of surgical procesdures can potentially be increased and trauma to patients reduced. Safety mechanisms can be implemented and system control improved.
The smallest 6-axis F/T sensor in the world
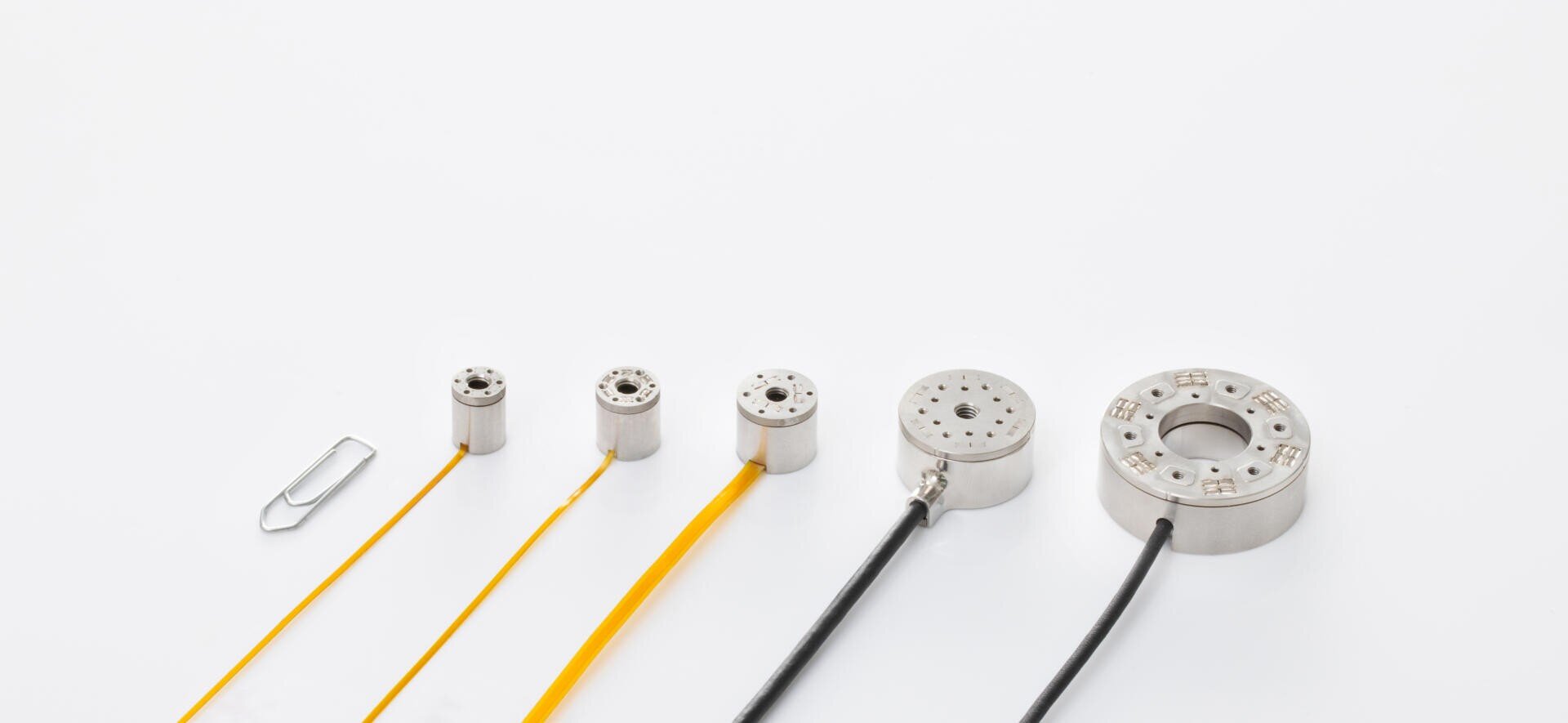
The Resense force/torque sensors measure forces and torques in all spatial directions. This is unique in the small design, up to a diameter of 8 mm.
In addition, the Resense sensors impress with their hollow shaft, which provides further advantages in the tight installation situations of robotic systems. The hollow shaft makes it possible to feed through cable harnesses or small tubes.
Dental, eye and abdominal surgery benefit from the Resense portfolio
Precision is particularly important in the head and abdominal areas. Only low forces may be exerted in many steps in order to avoid injuries during operations.
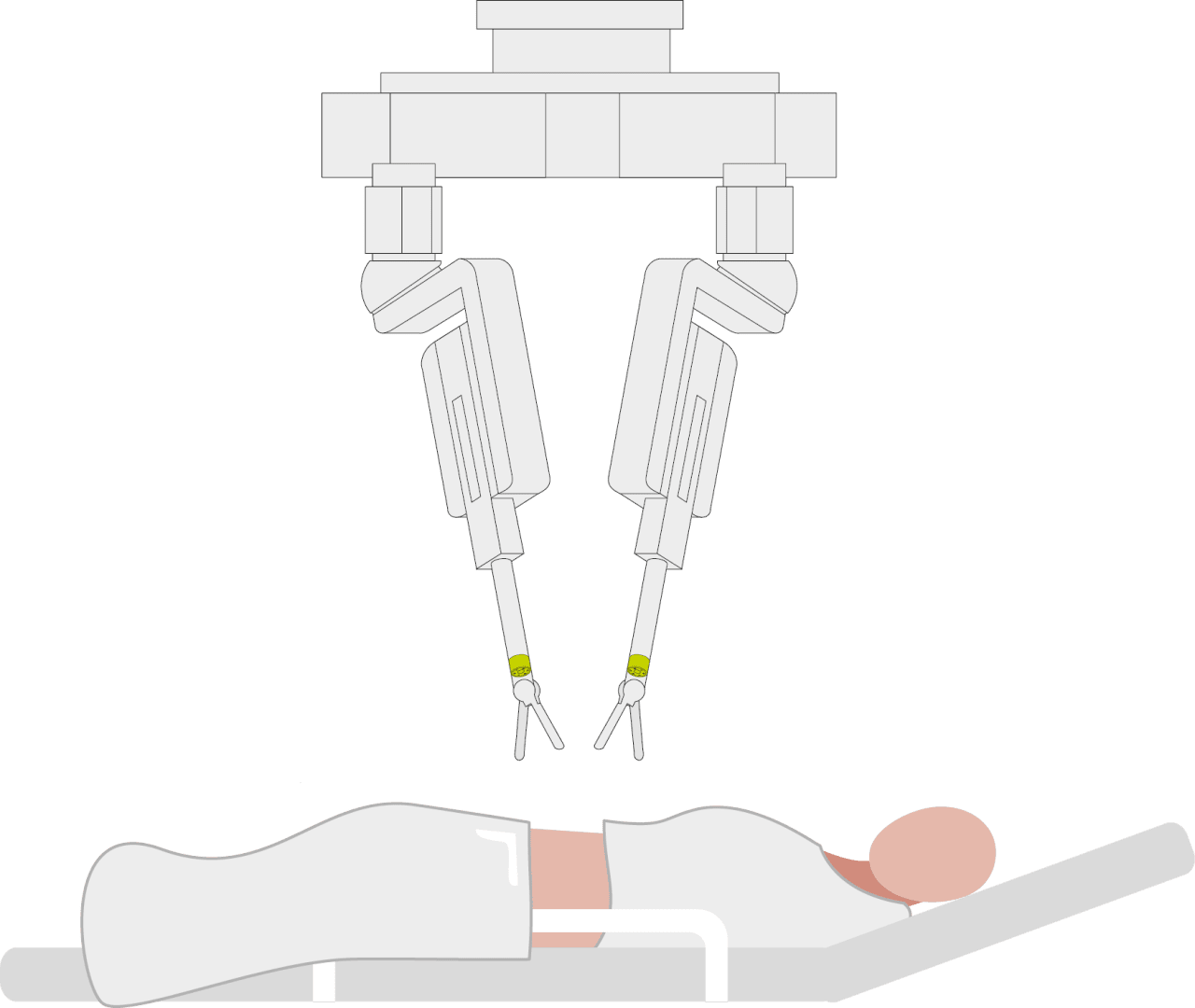
Robotic systems in these areas are different, and Resense sensors can be integrated into these systems in various forms. The smallest size, the HEX8 with an outer diameter of 8.4 mm, can be installed in the instrument tips and thus record data directly at the point of action. These are frequently used in abdominal surgery.
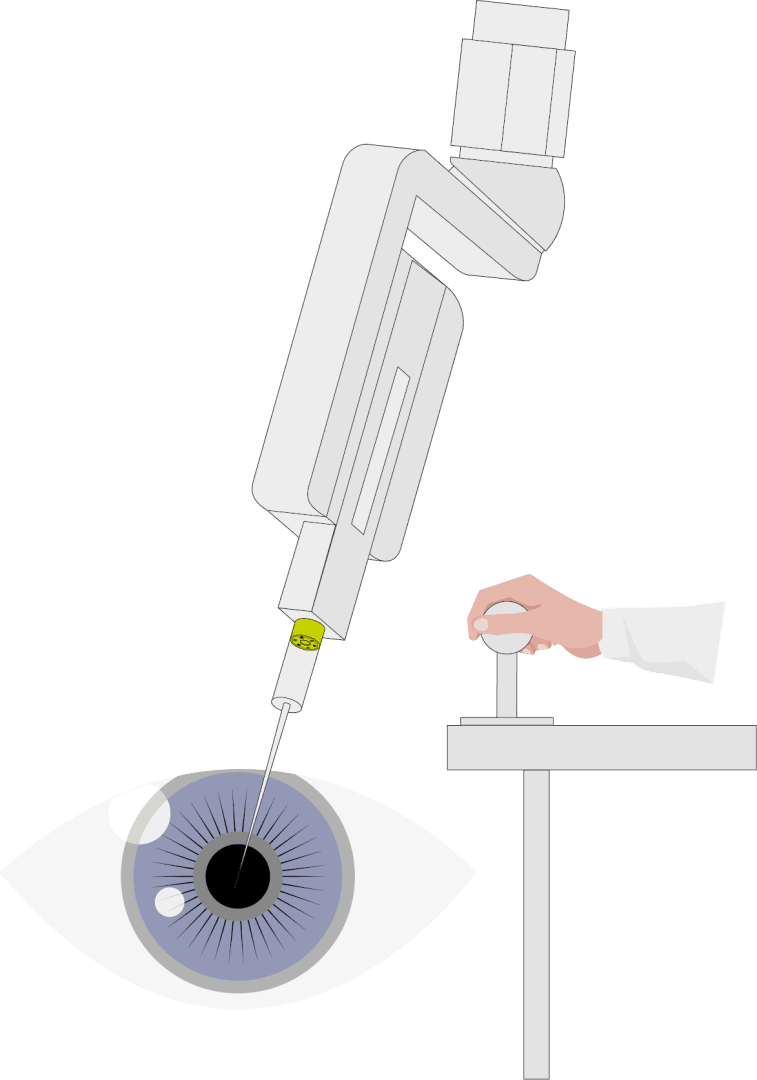
The installation of the other sizes in the end effector, as in our example in eye surgery, can also save space in the system. In addition, the hollow shaft can be used to insert a tube to introduce fluid into the eye.
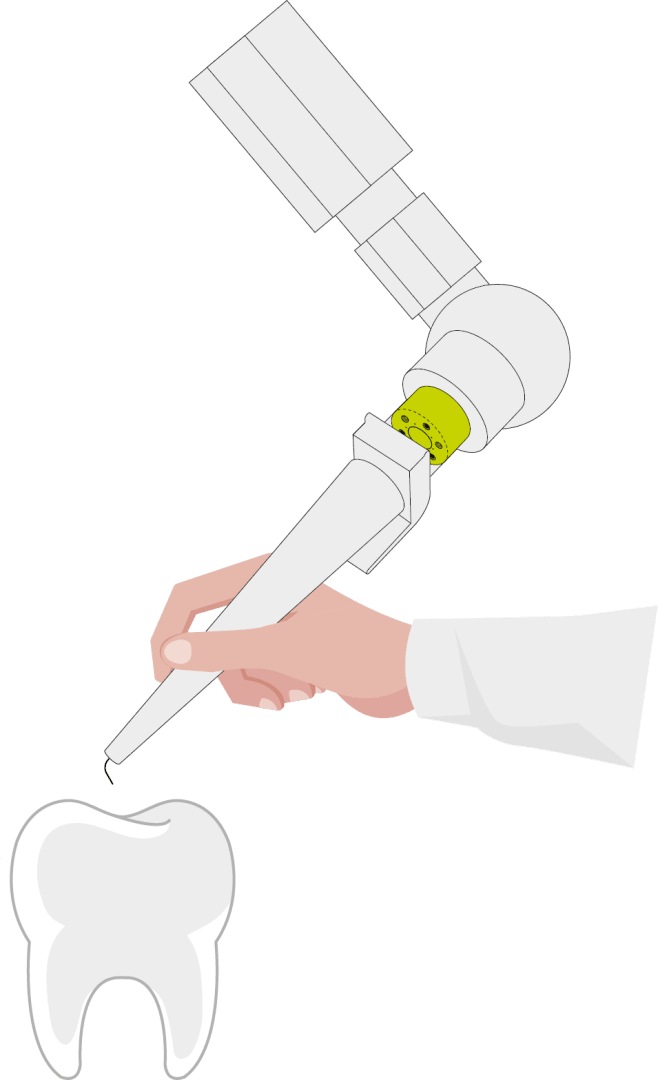
Hand-guided robotic systems also benefit from the monitoring of force/torque data. In the example of dental surgery, the HEX32, with an outer diameter of 32 mm, is mounted on the adapter from robot arm to end effector. The larger measuring range of up to 125 N is an advantage here.
Development and scaling partner WIKA & WITTENSTEIN
Resense sensors are developed and produced in collaboration with the partner companies WIKA and WITTENSTEIN.
As a joint venture, Resense works closely with the partner companies in various areas. The synergies with the sensor technology company WIKA are particularly evident in the area of development and production.
In close cooperation, the sensors are further developed for series production and production is scaled up. This will enable robot manufacturers to benefit from high volumes in the future.